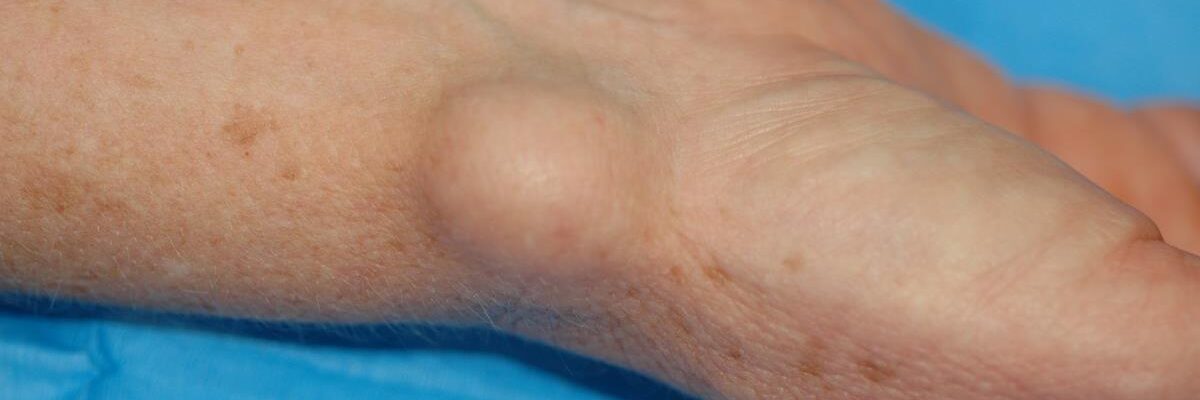
A ganglion cyst is a small, fluid-filled lump often found on the hands or wrists. The good news is that many ganglion cysts resolve on their own! Nearly half of all cases disappear without medical intervention. If the cyst is asymptomatic—causing no pain, discomfort, or movement limitations—it can simply be left alone.
However, if the ganglion cyst is bothersome or interferes with daily activities, there are medical procedures available to remove it. Here are the most common approaches:
- Observation and Non-Invasive Measures
- Watchful Waiting: If the cyst does not cause pain or other symptoms, monitoring its size and behavior is often enough.
- Immobilization: Using a wrist brace or splint may reduce movement and pressure on the affected area, potentially shrinking the cyst.
- Aspiration
This minimally invasive procedure involves:
- Puncturing the cyst with a sterile needle.
- Draining its jelly-like fluid using a syringe.
- Injecting a medication into the site to help prevent recurrence.
While simple, this method has a chance of the cyst returning over time.
- Surgical Removal
If the cyst is large, recurrent, or painful, surgical excision may be necessary. This procedure involves:
- Administering local anesthesia to the affected area.
- Removing the cyst along with its stalk to minimize recurrence.
Surgery is quick and typically performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to recover at home.
Important Precautions
- Avoid DIY Solutions: Never attempt to puncture or drain a ganglion cyst on your own using needles or sharp objects. Doing so increases the risk of infection or other complications.
- Consult a Doctor: Speak with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action tailored to your condition and financial situation.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
If the ganglion cyst becomes red, swollen, or painful, or if there are signs of infection such as fever or pus, consult a doctor immediately.