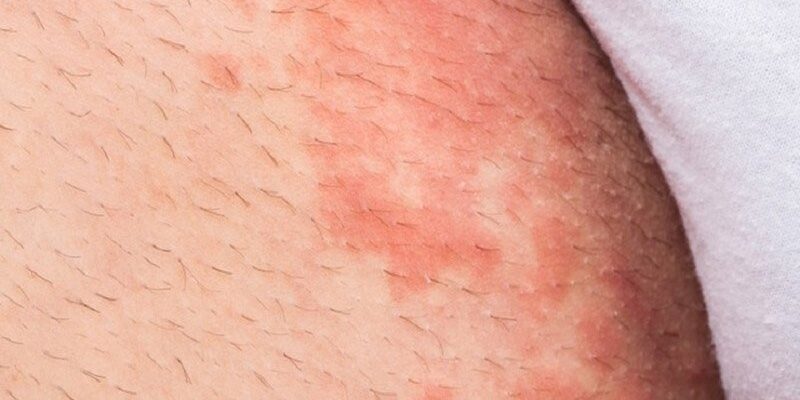
Jock itch, locally known as “hadhad,” is a common fungal skin infection caused by Tinea cruris. It often affects the groin area, inner thighs, and buttocks, leading to red, itchy, and sometimes scaly patches. Although it is not a serious condition, it can cause significant discomfort if not managed properly.
If you’re dealing with jock itch that hasn’t responded to common antifungal treatments like Trosyd or Canesten, there are still effective ways to address the condition. Here’s what you need to know about treating and managing jock itch:
Effective Treatments for Jock Itch
- Use Antifungal Medications.
Over-the-counter antifungal creams, powders, or sprays are often the first line of treatment. Look for products containing terbinafine, clotrimazole, or miconazole. These should be applied as directed, typically for one to two weeks, even if symptoms subside before completing the treatment. - Keep the Affected Area Dry and Clean.
Jock itch thrives in warm and moist environments, so keeping the groin area dry is crucial. After bathing, ensure the area is thoroughly dried. Use moisture-wicking underwear and avoid tight clothing to minimize sweating and friction. - Avoid Scratching.
Scratching the affected area can worsen the infection and increase the risk of secondary infections. Instead, use soothing powders or cooling creams recommended for fungal infections to relieve itchiness. - Try Prescription-Strength Antifungals.
If over-the-counter treatments do not work, consult a doctor for prescription-strength antifungal medications. These may include stronger topical treatments or oral antifungal medications like fluconazole or itraconazole, depending on the severity of the infection. - Maintain Proper Hygiene.
Regularly wash affected areas with mild soap and water. Change your clothes and underwear daily, especially after sweating. Disinfect personal items such as towels to prevent re-infection.
When to See a Doctor
If symptoms persist after using antifungal treatments for more than 10 days or worsen despite treatment, consult a healthcare professional. The symptoms might be caused by another underlying skin condition, such as eczema or psoriasis, that requires a different approach.
Preventing Jock Itch
Prevention is always better than cure. Practice good hygiene, keep the groin area dry, and wear loose, breathable clothing. Avoid sharing personal items like towels or sports gear, as these can spread the infection.
Jock itch may be stubborn, but with the right treatment and precautions, it can be effectively managed and prevented from recurring. If you’re unsure about the best treatment for your case, don’t hesitate to seek professional advice.