Tooth decay, commonly known as cavities or dental caries, is a prevalent dental issue that can lead to serious complications if not addressed promptly. Regular dental check-ups are essential for early detection and effective management of tooth decay. This article delves into the various examinations and diagnostic tools dentists employ to identify and assess tooth decay.
- Visual Examination
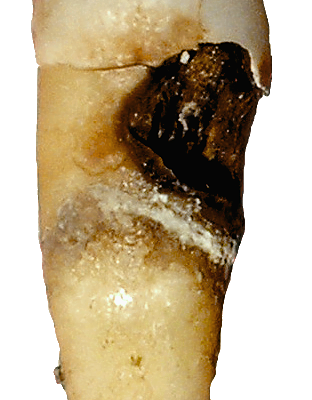
The initial step in diagnosing tooth decay involves a thorough visual inspection of the teeth and gums. Dentists look for signs such as discoloration, visible pits or holes, and plaque accumulation. They may also use a dental explorer, a specialized instrument, to gently probe the tooth surfaces for soft spots indicative of decay.
- Dental X-Rays
When visual examination is insufficient, dental X-rays become invaluable. These radiographic images allow dentists to detect decay between teeth and beneath existing fillings, areas not easily visible during a standard check-up. X-rays can also reveal the extent of decay and any potential bone loss associated with gum disease.
- Laser Fluorescence Devices
Advancements in dental technology have introduced laser fluorescence devices, such as DIAGNOdent. These tools emit a specific wavelength of light that interacts with the tooth structure, causing decayed areas to fluoresce differently than healthy enamel. This method aids in the early detection of cavities, especially in their initial stages.
- Fiber Optic Transillumination (FOTI)
FOTI involves shining a bright light through the tooth to identify changes in its structure. Decayed areas appear darker compared to healthy regions, assisting dentists in pinpointing cavities without the need for X-rays.
- Digital Imaging Fiber-Optic Trans-Illumination (DIFOTI)
An enhancement of FOTI, DIFOTI uses digital imaging to capture detailed pictures of the teeth. This technique is particularly useful for detecting early decay on the smooth surfaces of teeth.
- Quantitative Light-Induced Fluorescence (QLF)
QLF is a diagnostic method that uses fluorescent light to detect and quantify demineralization in tooth enamel. It helps in identifying early stages of decay and monitoring the effectiveness of preventive treatments.
- Electrical Conductance Measurement
This technique measures the electrical conductivity of tooth enamel. Decayed areas conduct electricity differently than healthy enamel, allowing for the detection of early carious lesions.
- Caries Detection Dyes
During restorative procedures, dentists may apply special dyes to the tooth surface. These dyes stain decayed areas, ensuring that all compromised tissue is removed before placing a filling.
Importance of Regular Dental Check-Ups
Early detection of tooth decay is crucial in preventing more severe dental issues. Regular dental visits enable timely intervention, which can save natural teeth and reduce the need for more invasive treatments. Dentists can also provide personalized advice on oral hygiene practices and dietary habits to minimize the risk of decay.
Preventive Measures
While diagnostic tools are essential, prevention remains the best approach to dental health. Maintaining good oral hygiene through regular brushing and flossing, reducing sugar intake, and using fluoride toothpaste can significantly lower the risk of tooth decay. Additionally, dental sealants and professional fluoride treatments offer extra protection, especially for individuals at higher risk.
In conclusion, understanding the various examinations for tooth decay empowers individuals to take proactive steps in maintaining their oral health. Regular dental check-ups, combined with good oral hygiene practices, are key to preventing and managing tooth decay effectively.