Overview
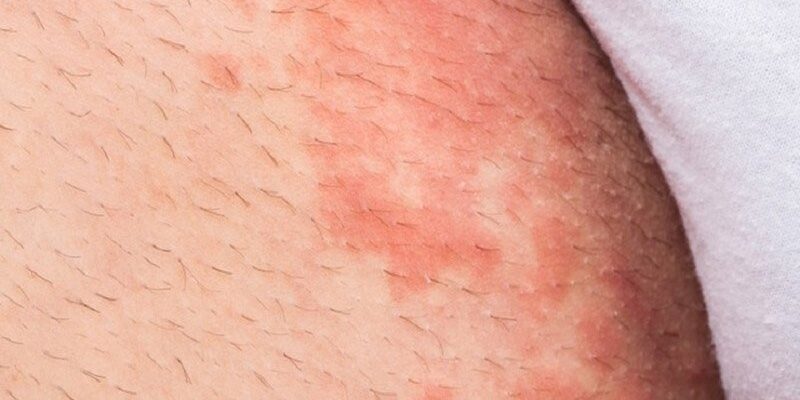
Jock itch, medically known as tinea cruris, is a common fungal infection that affects the groin area, inner thighs, and buttocks. It is caused by dermatophyte fungi, which thrive in warm, moist environments. The condition is more common in men but can also affect women, particularly athletes or individuals who sweat excessively or wear tight clothing for long periods.
The effects of jock itch include an itchy, red, and scaly rash that often develops in the folds of the skin. The rash may have a distinct border, sometimes appearing ring-shaped, and can cause discomfort or a burning sensation. In severe cases, the affected area may crack, ooze, or become secondarily infected with bacteria, leading to more serious symptoms.
Treatment for jock itch typically involves antifungal medications, which can be applied topically in the form of creams, powders, or sprays. Over-the-counter options like clotrimazole or miconazole are often effective, but prescription-strength antifungals may be required for persistent or severe cases. Keeping the affected area clean and dry is essential to promoting healing and preventing recurrence. In cases of bacterial infection, antibiotics may also be prescribed.
Most cases of jock itch resolve quickly with proper treatment and hygiene measures. Preventive strategies, such as wearing loose-fitting clothing, avoiding shared personal items, and maintaining good hygiene, are key to reducing the risk of recurrence. With timely care, individuals can manage and eliminate jock itch effectively, restoring comfort and skin health.
Table of Contents
When to See a Doctor
While jock itch can often be treated effectively with over-the-counter remedies and proper hygiene, certain situations warrant a visit to a medical professional to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Signs to see a doctor:
- Persistent symptoms. If the rash does not improve after two weeks of self-treatment with antifungal medications, it may require stronger prescription-strength treatments or further evaluation.
- Worsening condition. If the rash spreads, becomes more inflamed, or develops blisters, oozing, or cracking, it could indicate a secondary bacterial infection that needs medical attention.
- Severe itching or pain. Extreme discomfort or pain that interferes with daily activities should be evaluated by a healthcare provider to rule out complications.
- Recurring infections. Frequent bouts of jock itch may signal underlying issues such as compromised immunity or other fungal infections that need to be addressed.
- Uncertainty about the diagnosis. If the rash does not resemble typical jock itch or if it appears in unusual locations, a doctor can confirm the condition and rule out other skin disorders such as psoriasis, eczema, or intertrigo.
Consulting a healthcare professional in these cases ensures appropriate treatment and reduces the risk of complications or recurrence. Early intervention can lead to faster relief and better management of the condition.
What Type of Doctor to Seek
For jock itch, the first type of doctor to consult is a primary care physician or general practitioner. They can evaluate the rash, confirm the diagnosis, and recommend over-the-counter or prescription antifungal medications. They may also provide guidance on proper hygiene practices and preventive measures to avoid recurrence. If the condition appears severe or does not respond to initial treatments, your primary care doctor can refer you to a specialist for further care.
In more complex or recurring cases, it may be necessary to see a dermatologist, a doctor specializing in skin conditions. Dermatologists are equipped to handle stubborn fungal infections and can rule out other skin disorders that may mimic jock itch, such as psoriasis or eczema. They may also perform diagnostic tests like a skin scraping to identify the exact cause of the rash and tailor a more effective treatment plan. Consulting the right specialist ensures comprehensive care and better long-term management of the condition.
What to Expect from Your Visit to a Doctor
When visiting a doctor for jock itch, the appointment will typically begin with a discussion of your symptoms and medical history. The doctor will ask about the duration and severity of the rash, any associated symptoms like itching or burning, and whether you have tried over-the-counter treatments. They may also inquire about activities or habits that could contribute to the condition, such as excessive sweating, wearing tight clothing, or participating in sports.
During the physical examination, the doctor will closely inspect the affected area to confirm the diagnosis. If the rash does not appear typical of jock itch, they may take a small skin scraping for laboratory testing to identify the specific fungus or rule out other conditions like eczema or psoriasis. Based on the findings, the doctor will recommend an appropriate treatment plan, which may include topical or oral antifungal medications. For severe or recurrent cases, additional guidance on preventive measures and follow-up visits may also be provided to ensure effective management.
Jock Itch Treatment Options

Image Source: www.freepik.com
Jock itch, or tinea cruris, is a treatable condition, but the time it takes to heal depends on its severity. With proper care and treatment, most cases resolve within one to two weeks. Below is a list of effective remedies and treatments to speed up recovery:
Home Remedies and Over-the-Counter Treatments
- Daily bathing. Keeping the affected area clean and dry is essential. Shower daily to remove sweat and dirt from the groin and surrounding areas. Use cool or lukewarm water to soothe itching and ensure you dry the area thoroughly with a separate towel.
- Frequent clothing changes. Change clothes, especially underwear, frequently to prevent sweat and dirt buildup. Fresh clothing helps reduce the environment fungi need to thrive.
- Wearing loose-fitting clothing. Opt for loose, breathable fabrics to minimize irritation and allow the area to stay dry. Men can wear boxer shorts, while women can choose dresses or loose shorts instead of tight undergarments.
- Using antifungal creams. Apply over-the-counter antifungal creams such as terbinafine, clotrimazole, or miconazole to the affected area one or two times a day. Wash and dry the skin before application for the best results.
- Applying antifungal powder. Antifungal powders help reduce moisture and prevent fungal growth. They are particularly useful for people prone to sweating. Use them after bathing to keep the groin dry and fresh.
- Treating athlete’s foot. Jock itch often coexists with athlete’s foot. Treat both conditions simultaneously using antifungal creams to prevent reinfection.
Prescription Treatments and Medications
- Oral antifungal medication. For severe or recurrent cases, doctors may prescribe oral antifungal medications such as terbinafine, itraconazole, or fluconazole to address the infection from within.
- Topical steroids. If itching is severe, a doctor may recommend topical steroids like hydrocortisone to reduce inflammation and provide relief. These should be used only under medical supervision.
- Antibiotics. If scratching leads to bacterial infections in the affected area, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the secondary infection.
Natural Remedies
- Using akapulko leaves. This medicinal plant, approved by the Department of Health, is known for its antifungal properties. Crush fresh akapulko leaves, extract the juice, and apply it to the affected area once or twice a day.
With consistent treatment and proper hygiene, most cases of jock itch heal quickly and completely. If symptoms persist beyond two weeks or worsen despite treatment, it is advisable to consult a dermatologist for further evaluation and care.
Jock Itch Prognosis
The prognosis for jock itch is generally excellent with proper treatment and hygiene. Most cases resolve within a few weeks, and the recurrence can be minimized by following preventive measures. Below is an overview of the expected outcomes for each treatment option:
- Daily bathing and hygiene. Regular cleaning and drying of the affected area provide immediate relief from itching and prevent the spread of the infection. Consistent hygiene significantly reduces the risk of recurrence.
- Frequent clothing changes and loose-fitting clothing. These measures create an environment less favorable for fungal growth, improving comfort and speeding up recovery.
- Antifungal creams and powders. Topical antifungals are highly effective at eliminating fungi when applied consistently. Most patients experience noticeable improvement within a week.
- Oral antifungal medications. For severe or persistent cases, oral antifungals treat the infection at its root, often leading to complete resolution within two to four weeks.
- Topical steroids. These quickly reduce inflammation and itching, providing symptom relief while antifungal treatments address the underlying infection.
- Natural remedies like akapulko. These can complement medical treatments, especially for mild cases, and are effective when used correctly and regularly.
- Antibiotics for secondary infections. If bacterial infections occur due to scratching, antibiotics effectively treat these complications, restoring skin health.
By adhering to the recommended treatments and preventive measures, most individuals recover fully without complications. For the best outcomes, early intervention and consistent follow-up care are essential.