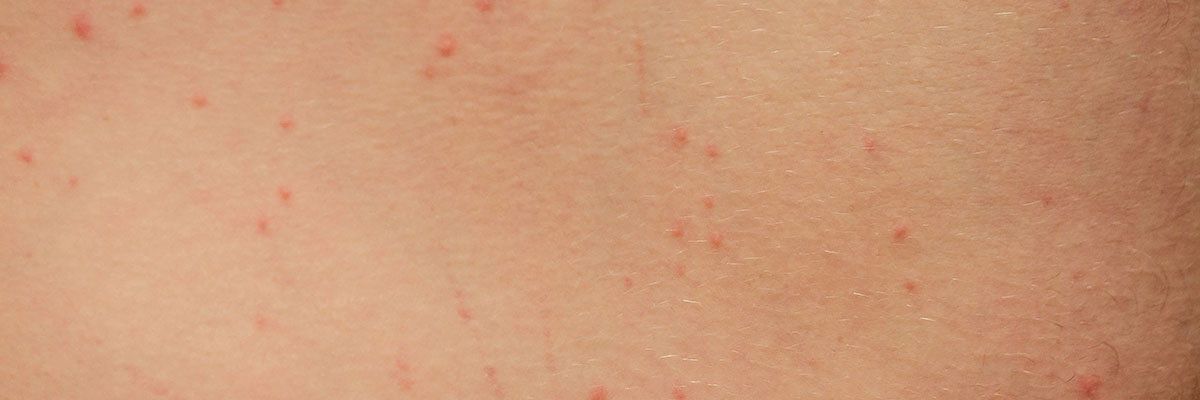
Overview
Bed bug bites are skin irritations caused by Cimex lectularius, commonly known as bed bugs. These small, parasitic insects feed on the blood of humans and animals, typically during the night while their host is sleeping. Bed bugs are often found in mattresses, furniture, and small crevices, making them difficult to detect and eliminate. Although their bites are not known to transmit diseases, they can cause significant discomfort and emotional stress.
The effects of bed bug bites vary from person to person. Most bites appear as small, red, itchy welts, often arranged in a cluster or line. For some individuals, the bites may cause only mild irritation, while others may experience more severe allergic reactions, such as swelling, blisters, or intense itching. Scratching the bites can lead to secondary infections, which may require medical treatment. In addition to physical symptoms, bed bug infestations often cause anxiety, insomnia, and stress due to the fear of being bitten.
Treatment for bed bug bites focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. Over-the-counter antihistamines or topical corticosteroids can reduce itching and inflammation. Applying cold compresses to the affected areas also provides relief. For more severe reactions or infections, a healthcare provider may prescribe stronger medications or antibiotics. It is equally important to address the infestation to prevent further bites.
Eliminating bed bugs requires a comprehensive approach. This includes thoroughly cleaning bedding, vacuuming mattresses and furniture, sealing crevices, and using professional pest control services when necessary. Bed bug infestations can be persistent, so it is essential to act quickly and consistently to eradicate them completely. With proper treatment and management, the physical and emotional effects of bed bug bites can be alleviated.
Table of Contents
When to See a Doctor
While bed bug bites are often mild and manageable at home, there are situations where seeking medical attention is necessary. Prompt consultation with a healthcare professional can help address severe reactions or complications associated with the bites.
Signs to see a doctor:
- Severe allergic reactions. If you experience intense swelling, redness, or blistering at the site of the bites, it may indicate an allergic reaction that requires medical treatment, such as antihistamines or corticosteroids.
- Signs of infection. Persistent redness, warmth, pain, or pus around the bite area can indicate a secondary infection caused by scratching. This requires medical evaluation and potentially antibiotics.
- Systemic symptoms. If you develop fever, chills, or swollen lymph nodes alongside the bites, it could indicate a more serious complication that needs immediate attention.
- Difficulty managing symptoms. If itching or discomfort persists despite using over-the-counter remedies, a doctor can recommend stronger treatments to relieve symptoms.
- Pre-existing skin conditions. Individuals with eczema, psoriasis, or other skin conditions should consult a healthcare provider if bed bug bites worsen their symptoms or lead to complications.
Seeking medical advice ensures that any serious reactions or infections are addressed promptly, reducing the risk of long-term complications and improving comfort during recovery.
What Type of Doctor to Seek

If you experience bed bug bites and need medical attention, your first point of contact should be a primary care physician or a general practitioner. These doctors can evaluate your symptoms, determine if there are signs of an allergic reaction or infection, and recommend appropriate treatments. For mild cases, they may suggest over-the-counter remedies or prescribe medications such as antihistamines, corticosteroid creams, or antibiotics for infections caused by scratching.
In more severe cases, or if the bites lead to significant skin issues, you may be referred to a dermatologist. Dermatologists specialize in skin conditions and can provide advanced care for allergic reactions, persistent irritation, or secondary infections caused by bed bug bites. They can also help distinguish bed bug bites from other insect bites or skin conditions that may look similar, ensuring you receive accurate treatment. Seeking the right medical expertise ensures that both the physical and emotional effects of bed bug bites are managed effectively.
What to Expect from Your Visit to a Doctor
When visiting a doctor for bed bug bites, you can expect a thorough assessment to determine the severity of your condition and identify any complications. The doctor will begin by asking about your symptoms, including when the bites appeared, how they have progressed, and whether you have experienced itching, swelling, or pain. They may also inquire about potential exposure to bed bugs, such as recent travel, the condition of your home environment, or reports of infestations in places you frequent.
The doctor will perform a physical examination of the affected areas to assess the bites and check for signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, or pus. Depending on the findings, they may recommend treatment options such as antihistamines for itching, corticosteroid creams to reduce inflammation, or antibiotics for infected bites. In cases of severe allergic reactions, they may prescribe oral corticosteroids or other medications to manage symptoms. Additionally, the doctor may offer guidance on preventing future bites, including tips on bed bug eradication and home hygiene. If necessary, they might refer you to a dermatologist for specialized care.
Bed Bug Bites Treatment Options
Bed bug bites can heal on their own within one to two weeks, but there are several remedies that can help relieve discomfort and speed up recovery. Below are effective treatments, including home remedies and medications, to manage the itching, swelling, and potential complications associated with bed bug bites.

Treatments for Bed Bug Bites
- Wash the affected areas. Gently clean the bites with soap and clean water. Washing reduces itching, removes any bacteria or allergens, and lowers the risk of infection. Regular cleansing is an essential first step for managing bed bug bites effectively.
- Apply steroid cream. Over-the-counter steroid creams, such as hydrocortisone, can help reduce itching and inflammation. Stronger formulations may require a doctor’s prescription. Pregnant women should consult a doctor to ensure the chosen cream is safe for both the mother and baby.
- Take oral antihistamines. Medications like diphenhydramine are helpful for reducing itching, especially if it interferes with sleep. For more severe allergic reactions, a doctor may prescribe stronger antihistamines to manage symptoms.
- Use pain relievers. If excessive scratching causes pain, wounds, or skin irritation, over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage discomfort and promote healing.
- Apply an antiseptic solution or take antibiotics for infection. If the bites become infected, a doctor may prescribe topical antiseptics to clean the area or oral antibiotics to treat the infection. This step is particularly important if there are signs of worsening redness, swelling, or pus.
- Use a cold compress or ice pack. Applying a cold towel or ice pack to the affected areas can numb the skin, reduce inflammation, and provide quick relief from itching and swelling.
- Apply a baking soda paste. Baking soda’s alkaline properties can help neutralize skin acidity, reducing itching and swelling. Mix one tablespoon of baking soda with a small amount of water to create a paste, then apply it to the bites.
- Avoid scratching. Refrain from scratching the bites to prevent breaking the skin and causing infection. Instead, take a warm bath or shower to soothe the irritation and reduce the urge to scratch.
If symptoms persist or worsen within one to two weeks despite these treatments, it’s important to consult a doctor. Seek medical attention immediately if the bites spread, develop pus, or cause significant swelling, as these may indicate an infection or a more severe allergic reaction.
Bed Bug Bites Prognosis
The prognosis for bed bug bites is generally positive, with most cases resolving within one to two weeks with proper care. Effective treatments can alleviate discomfort, prevent complications, and speed up recovery. Below is an overview of the expected outcomes for each treatment option.
- Washing the affected areas. Regularly cleaning the bites with soap and water significantly reduces the risk of infection and soothes irritation, promoting faster healing.
- Applying steroid creams. Topical corticosteroids effectively reduce inflammation and itching, providing relief within a few hours to a couple of days. With consistent use, swelling and redness usually subside quickly.
- Taking oral antihistamines. Antihistamines are highly effective in reducing itching and improving sleep quality. They also help manage mild allergic reactions, ensuring a more comfortable recovery.
- Using pain relievers. Over-the-counter pain medications ease discomfort caused by excessive scratching or inflamed bites, making it easier for the skin to heal without interference.
- Treating infections with antibiotics or antiseptics. Prompt use of antiseptics or prescribed antibiotics effectively treats infections, preventing further complications and ensuring a complete recovery.
- Applying cold compresses or ice packs. Cold therapy offers immediate relief from itching and swelling, reducing the likelihood of scratching and associated complications.
- Using a baking soda paste. This home remedy can neutralize skin acidity and provide soothing relief, improving the healing process for mild bites.
- Avoiding scratching. Refraining from scratching minimizes the risk of infections or scarring, leading to a smoother and quicker recovery.
With the right combination of treatments, most individuals recover fully from bed bug bites without long-term effects. Following these remedies consistently ensures faster healing, and seeking medical advice for persistent symptoms can address complications effectively.