Overview
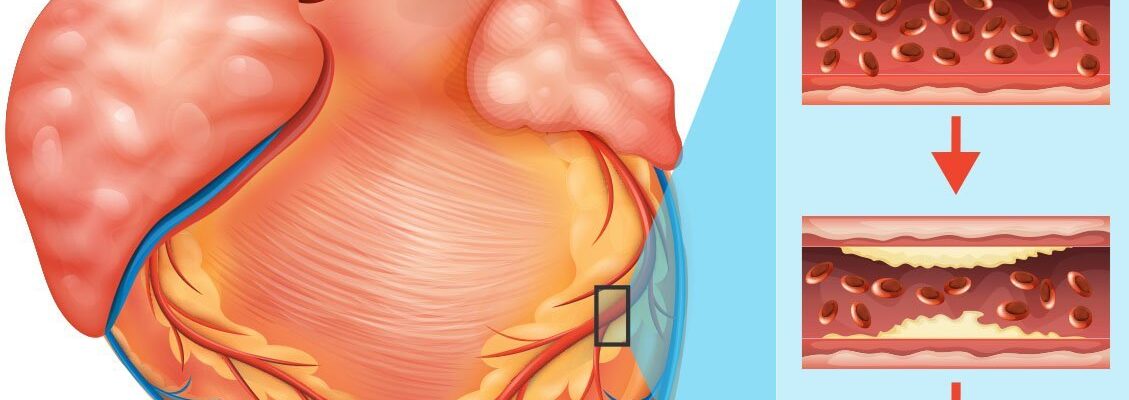
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a condition where the coronary arteries, which supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart, become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaque (a mixture of fat, cholesterol, and other substances). This restricts blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to symptoms like chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, and, in severe cases, heart attacks.
CAD is a leading cause of heart disease and can develop over many years. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications, including heart failure or arrhythmias. Treatments for coronary artery disease aim to restore proper blood flow to the heart and prevent complications. These include lifestyle changes, medications, medical procedures such as angioplasty or stenting, and, in advanced cases, surgery like coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
Managing CAD often requires a combination of these treatments to improve heart function, alleviate symptoms, and reduce the risk of heart attacks.
Table of Contents
When to See a Doctor
If you suspect you may have coronary artery disease (CAD), it’s important to seek medical attention early, as this condition can lead to serious complications like heart attacks. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. You should consider seeing a doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Chest pain or discomfort (angina), especially during physical activity or stress
- Shortness of breath with minimal exertion
- Fatigue or weakness that interferes with daily activities
- Heart palpitations or irregular heartbeats
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
Additionally, if you have risk factors for CAD, such as a family history of heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, or high cholesterol, it’s advisable to consult a doctor for a thorough evaluation, even if you do not currently have symptoms.
Who to Consult
For coronary artery disease, you should start by seeing your primary care physician or family doctor, who can assess your risk factors, perform initial evaluations, and refer you to a specialist if needed. The specialist typically involved in diagnosing and managing CAD is a cardiologist, a doctor specializing in heart conditions.
What to Expect from Your Doctor’s Visit
During your visit, your doctor will:
- Take a detailed medical history: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, lifestyle habits (such as diet and exercise), family history of heart disease, and any risk factors like smoking, high blood pressure, or diabetes.
- Perform a physical examination: Your doctor will check your heart rate, blood pressure, and listen to your heart and lungs for any abnormalities.
- Order diagnostic tests: Depending on your symptoms and risk factors, your doctor may recommend tests to assess the health of your heart and arteries, including:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to measure the heart’s electrical activity.
- Stress test to monitor your heart function during physical exertion.
- Blood tests to check for cholesterol levels, blood sugar, and markers of heart disease.
- Echocardiogram to evaluate heart structure and function.
- Coronary angiography or CT scan to visualize any blockages in your coronary arteries.
Based on the results, your doctor will discuss treatment options and recommend lifestyle changes, medications, or further interventions such as angioplasty or surgery, depending on the severity of the condition.
Treatment Options
Treating coronary artery disease (CAD) focuses on improving blood flow to the heart, reducing symptoms, preventing complications, and addressing the underlying causes. Treatment often involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and medical procedures, depending on the severity of the condition and individual risk factors.
Here are the main treatment options for CAD:
-
Lifestyle Changes
- Heart-Healthy Diet. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce cholesterol levels and prevent plaque buildup in the arteries. Limiting saturated fats, trans fats, and sodium is also important for heart health.
- Regular Exercise. Engaging in moderate physical activity (such as walking, swimming, or cycling) for at least 150 minutes per week can improve heart function and help maintain a healthy weight.
- Quitting Smoking. Smoking significantly increases the risk of CAD by damaging the arteries and promoting plaque formation. Quitting smoking is essential for reducing the risk of heart attacks and improving overall heart health.
- Managing Stress. Chronic stress can contribute to heart disease by raising blood pressure and promoting unhealthy behaviors. Stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or therapy can help reduce its impact on heart health.
-
Medications
- Cholesterol-Lowering Drugs. Statins, such as atorvastatin and simvastatin, are commonly prescribed to reduce cholesterol levels, slow plaque buildup, and prevent heart attacks. Other medications, like ezetimibe or PCSK9 inhibitors, may also be used for high-risk patients.
- Antiplatelet Drugs. Medications like aspirin and clopidogrel help prevent blood clots by thinning the blood. This reduces the risk of a heart attack or stroke by keeping arteries open.
- Beta-Blockers. These medications lower heart rate and blood pressure, reducing the heart’s workload and helping to relieve chest pain (angina).
- ACE Inhibitors and ARBs. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) help relax blood vessels, lower blood pressure, and reduce the strain on the heart.
- Nitroglycerin. This medication is often used to quickly relieve chest pain by relaxing and widening blood vessels, improving blood flow to the heart muscle.
-
Medical Procedures
- Angioplasty and Stenting. Angioplasty involves using a balloon to widen narrowed or blocked coronary arteries, followed by placing a stent (a small mesh tube) to keep the artery open. This restores blood flow and relieves symptoms like chest pain.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG). In more severe cases, bypass surgery may be needed. This involves taking a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body and grafting it onto the blocked artery, allowing blood to bypass the blockage.
- Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP). This non-invasive therapy involves inflating cuffs around the legs to improve blood flow to the heart. It’s typically used for patients who are not candidates for surgery or angioplasty but still experience angina.
-
Treating Underlying Conditions
- Diabetes Management. Controlling blood sugar levels through medications, diet, and exercise can significantly reduce the risk of CAD and prevent complications.
- Hypertension Control. Managing high blood pressure with lifestyle changes and medications like ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, or calcium channel blockers is essential for reducing stress on the heart.
- Weight Loss for Obesity. Weight loss through diet and exercise can reduce the strain on the heart, improve cholesterol and blood pressure levels, and decrease the risk of further plaque buildup.
Coronary artery disease requires a multifaceted treatment approach tailored to the individual’s condition and risk factors. From lifestyle changes and medications to advanced procedures like angioplasty and bypass surgery, managing CAD involves a combination of therapies to improve heart function and prevent future heart events. Working closely with a healthcare team is key to developing a personalized treatment plan and ensuring long-term heart health.
Prognosis
The prognosis for coronary artery disease (CAD) varies depending on the treatment approach, the severity of the disease, and how well the patient follows the recommended care plan. While CAD is a chronic condition, appropriate treatment can significantly improve quality of life and reduce the risk of serious complications such as heart attacks. Below is an overview of the prognosis for each major treatment option.
-
Lifestyle Changes
- Prognosis: Patients who adopt heart-healthy habits, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking, often see a significant improvement in their symptoms and a reduced risk of heart attacks. Long-term lifestyle changes can slow disease progression and improve overall heart health, making this a critical component of CAD management.
-
Medications
- Prognosis: With proper adherence, medications like statins, beta-blockers, and antiplatelet drugs can effectively control symptoms, lower cholesterol levels, and reduce the likelihood of heart attacks and strokes. Medication therapy helps stabilize plaque in the arteries, preventing further blockages and complications.
-
Angioplasty and Stenting
- Prognosis: Angioplasty with stenting typically provides immediate symptom relief, especially for chest pain. It’s a minimally invasive procedure with a good success rate, but patients may still need long-term lifestyle changes and medications to maintain heart health. In some cases, blockages may recur, necessitating further interventions.
-
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
- Prognosis: Bypass surgery has a very favorable long-term prognosis, especially for patients with severe or widespread artery blockages. Many patients experience significant relief from symptoms and a lower risk of heart attacks. However, as with all treatments, lifestyle management and medication adherence remain essential to ensure lasting benefits.
-
Treating Underlying Conditions
- Prognosis: Managing conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and obesity can drastically improve heart function and lower the risk of CAD complications. With well-controlled blood sugar, blood pressure, and body weight, patients often experience fewer symptoms and a better long-term outlook.
While CAD is a lifelong condition, effective treatments can greatly improve the prognosis and overall quality of life. Whether through lifestyle changes, medications, or medical procedures, adhering to a personalized treatment plan can help prevent complications and promote a healthier heart. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are crucial for monitoring progress and adjusting treatments as needed.