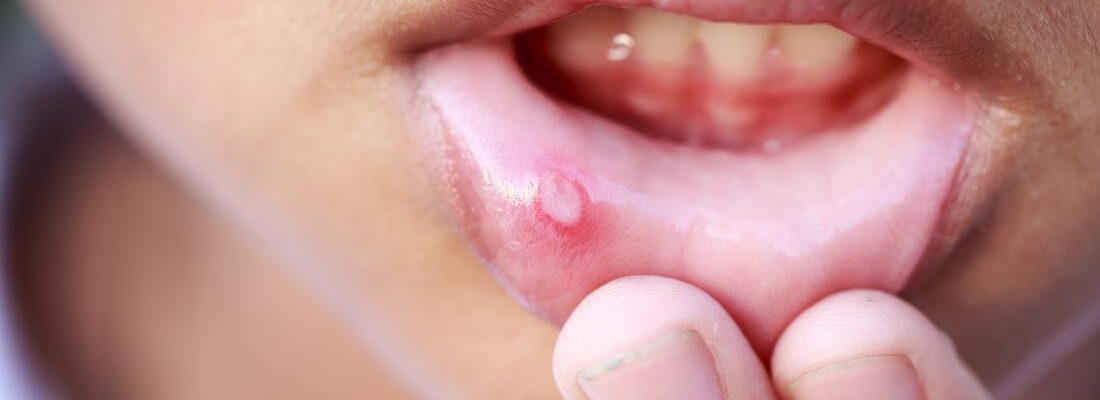
Canker sores, also known as mouth sores or “singaw,” commonly cause a stinging or painful sensation in the affected area inside the mouth. These sores typically last for 5 to 10 days before healing on their own. They often appear as white patches or ulcers surrounded by a red, inflamed area. Usually, canker sores do not require professional medical examination because they are easily identified through these symptoms.
Common Symptoms:
- Painful sores inside the mouth: These can appear on the tongue, inner cheeks, gums, or lips.
- Burning or tingling sensation: Often felt before the sores emerge.
- Round, white or gray ulcers: With a red border around them.
- Discomfort while eating or speaking: Especially when consuming spicy or acidic foods.
Possible Causes:
While the exact cause of canker sores is not always clear, several factors may contribute to their development:
- Minor mouth injuries: From dental work, aggressive brushing, or accidental bites.
- Food sensitivities: Particularly to acidic or spicy foods like citrus fruits or tomatoes.
- Stress and hormonal changes: Emotional stress or hormonal shifts during menstruation.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Lack of vitamin B12, zinc, iron, or folic acid.
- Allergic responses: To certain bacteria in the mouth.
- Underlying health conditions: Such as celiac disease or inflammatory bowel diseases.
When Should You See a Doctor?
You should consider consulting a doctor or dentist if you experience the following:
- Appearance after medication use: If the canker sore emerged after taking certain drugs.
- Sores that enlarge or spread: Growing sores that extend to other parts of the mouth.
- Frequent recurrence: If the sores keep coming back frequently.
- Prolonged duration: Sores lasting longer than two weeks.
- Accompanying severe symptoms:
- Fever
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking
- Excessive drooling
- Skin rashes or hives
- Unexplained weight loss
Importance of Medical Consultation:
Persistent or severe canker sores may indicate an underlying health issue that requires medical attention. A healthcare professional can provide appropriate treatment, which may include:
- Topical medications: Prescription creams, gels, or liquids to ease pain and speed healing.
- Mouth rinses: Antimicrobial or steroid mouthwashes to reduce inflammation.
- Oral medications: In cases of severe or persistent sores.
- Investigations for underlying conditions: Tests to rule out nutritional deficiencies or immune system problems.
Tips for Managing Canker Sores at Home:
- Avoid irritating foods: Stay away from spicy, acidic, or rough-textured foods that can aggravate sores.
- Maintain good oral hygiene: Gently brush your teeth with a soft-bristled toothbrush and use mild toothpaste.
- Use protective coverings: Over-the-counter topical products can form a protective layer over the sores.
- Rinse with saltwater: A mild saltwater rinse can help reduce discomfort and promote healing.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep the mouth moist and support the healing process.
Preventive Measures
- Manage stress: Practice relaxation techniques like meditation or deep-breathing exercises.
- Balanced diet: Ensure adequate intake of essential vitamins and minerals.
- Avoid known triggers: If certain foods or products cause sores, eliminate them from your diet or routine.
- Protect your mouth: Be cautious when eating hard foods and consider using a mouthguard if you grind your teeth at night.
While canker sores are generally harmless and resolve on their own, they can cause significant discomfort. Paying attention to the symptoms and knowing when to seek medical advice can help manage the condition effectively. If you’re experiencing persistent or unusually severe mouth sores, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.