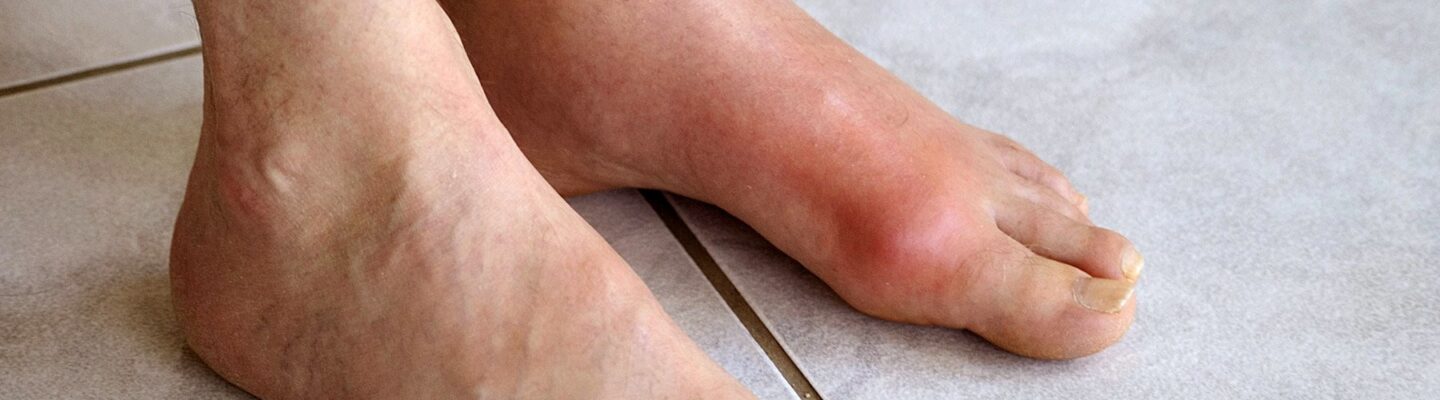
Uric acid is a natural byproduct of the breakdown of purines, compounds found in certain foods and drinks, as well as in the body’s own cells. While it is normal to have uric acid in the body, excessive levels in the blood—a condition known as hyperuricemia—can lead to health problems, including gout, a form of inflammatory arthritis.
How Is Uric Acid Measured?
The level of uric acid in the blood can be determined through a blood chemistry test. This test involves drawing 2-5 mL of blood, typically from a vein in the arm near the elbow. Results are often available within a few hours. Regular testing may be recommended for individuals experiencing symptoms of gout, kidney stones, or other conditions linked to high uric acid.
What Are Normal Uric Acid Levels?
According to medical experts, normal uric acid levels are as follows:
- Men: 3.6–8.3 mg/dL (214–494 µmol/L)
- Women: 2.3–6.6 mg/dL (137–393 µmol/L)
Levels above these ranges may indicate hyperuricemia and require medical attention.
How to Prevent High Uric Acid Levels

Managing uric acid levels is essential to reducing the risk of gout and other complications. Below are effective strategies:
- Avoid Alcohol. Alcohol, particularly beer and spirits, increases uric acid production and reduces its excretion, leading to elevated levels in the blood.
- Limit Foods High in Purines. Avoid purine-rich foods, such as organ meats (liver, kidney), red meat, shellfish, and certain types of fish like sardines and anchovies. These foods contribute to increased uric acid production.
- Consume Foods That Lower Uric Acid. Incorporate foods known to help reduce uric acid levels, such as cherries, strawberries, and citrus fruits. Hydration is also key—drink plenty of water to support kidney function and the excretion of uric acid.
Foods to Avoid for High Uric Acid
Certain foods are especially high in purines and should be avoided or minimized:
- Organ meats (e.g., liver, kidney)
- Shellfish (e.g., shrimp, crabs, clams)
- Red meats (e.g., beef, lamb, pork)
- Fatty fish (e.g., sardines, mackerel)
- Alcoholic beverages, particularly beer and spirits
Foods That Help Reduce Uric Acid
To manage uric acid levels, include the following in your diet:
- Cherries and Berries: These fruits contain compounds that help reduce inflammation and uric acid levels.
- Citrus Fruits: Oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are rich in Vitamin C, which can lower uric acid levels.
- Green Leafy Vegetables: Spinach, kale, and broccoli provide antioxidants that combat hyperuricemia.
- Water and Hydrating Fluids: Drinking sufficient water helps the kidneys filter and excrete uric acid efficiently.
High uric acid levels can lead to gout and other complications, but they are manageable with proper lifestyle changes and dietary adjustments. Avoiding alcohol and purine-rich foods, staying hydrated, and including uric acid-lowering foods in your diet are key to maintaining healthy levels. If you experience symptoms like joint pain or swelling, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate evaluation and treatment. Regular monitoring and proactive measures can help prevent long-term complications associated with hyperuricemia.