Filipinos have a natural love for sweet foods. From a sugary taho for breakfast to tocino and longganisa for meals, and banana cue, halo-halo, or sweet dipping sauces for snacks, sweet flavors are deeply embedded in Filipino culture. However, consuming too much sugar daily can have serious health consequences. Studies have shown that excessive sugar intake can lead to various diseases, and the initial enjoyment may eventually be replaced with the bitterness of health problems.
-
Tooth Decay

Tooth decay is a widespread problem among both children and adults in the Philippines, largely due to the excessive consumption of sugary foods. The bacteria naturally present in the mouth feed on sugar residues left on the teeth, producing acids that erode enamel and cause cavities. Regular oral hygiene practices and reducing sugar intake are essential for preventing tooth decay.
-
Liver Damage
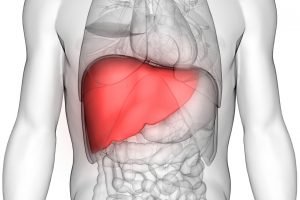
Understanding the connection between sugar and liver health begins with how sugar is metabolized. Sugars consumed in food are broken down into glucose and fructose. Glucose is used for energy, while fructose is processed in the liver, where it is converted to glycogen for storage. However, the liver’s glycogen storage capacity is limited. When fructose intake exceeds this capacity, the excess is turned into fat, leading to a condition known as fatty liver disease. Over time, this can progress to liver damage.
-
Weight Gain and Obesity

Excess sugar is stored in the body as fat when not used for energy. This accumulation not only occurs in the liver but also in various parts of the body, contributing to weight gain. Over time, this can lead to obesity, a condition that increases the risk of several chronic diseases, including diabetes, heart disease, and hypertension.
-
Diabetes
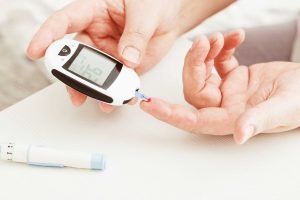
A diet consistently high in sugar increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Over time, excessive sugar intake can lead to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells fail to effectively absorb glucose from the bloodstream. This disrupts normal metabolic processes, resulting in persistently high blood sugar levels—a hallmark of diabetes.
-
Bone Weakness
A study published in Nutrition Reviews in June 2008 highlighted the link between excessive sugar intake and bone fragility. Prolonged consumption of high amounts of sugar may contribute to insulin resistance, which in turn affects calcium metabolism and bone density. This raises the risk of fractures and other bone-related issues.
-
Cancer
Cancer is characterized by the rapid and uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells. Studies suggest that high blood sugar levels may create an environment conducive to the growth of cancer cells. Excess sugar in the diet has been linked to an increased risk of certain types of cancer.
-
High Cholesterol Levels
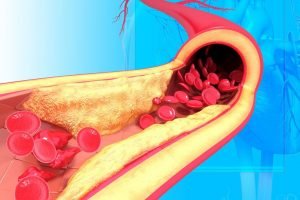
A study published in The Journal of the American Medical Association in April 2010 found that excessive sugar consumption lowers levels of good cholesterol (HDL) while raising levels of bad cholesterol (LDL). Elevated LDL cholesterol contributes to the development of heart disease and high blood pressure.
How to Avoid the Negative Effects of Excess Sugar
- Limit Sugary Foods and Drinks. Cut back on desserts, sweetened beverages, and processed foods.
- Choose Healthier Alternatives. Opt for naturally sweetened options or foods with lower glycemic indexes.
- Practice Portion Control. Reducing serving sizes helps minimize overall sugar intake.
- Maintain Regular Exercise. Physical activity helps burn excess sugar and fat in the body.
- Stay Informed. Read labels and be mindful of hidden sugars in packaged foods.
While sugar adds flavor to many foods and drinks, consuming it in excess can lead to serious health problems. By moderating sugar intake, making healthier food choices, and maintaining an active lifestyle, you can prevent the harmful effects of excess sugar and support long-term health and well-being.


