Vitamin A is an essential nutrient that plays a significant role in maintaining good eyesight, strengthening the immune system, and supporting the production of new cells in the body. Also known as Retinoid, Vitamin A comes in two forms: Performed Vitamin A, found in animal products like milk, fish, and meat, and Provitamin A carotenoids, derived from fruits and vegetables. Vitamin A is vital for preventing diseases like cancer and measles, as well as addressing age-related vision problems.
Importance of Vitamin A in the Body
Vitamin A is crucial for maintaining healthy vision. It aids the protein rhodopsin in allowing the eye’s receptors to function properly, particularly in low-light conditions. Additionally, Vitamin A plays a role in cell production, reducing the risk of certain cancers.
Daily Vitamin A Requirements
The recommended Daily Value (DV) for Vitamin A is 5,000 International Units (IU). However, this amount may vary depending on life stages, such as pregnancy or aging.
Effects of Excessive Vitamin A
As a fat-soluble vitamin, excess Vitamin A is stored in the liver. Overconsumption may lead to liver damage, nausea, vomiting, and hair loss. For adults, the maximum tolerable intake is 10,000 IU per day.
Effects of Vitamin A Deficiency
A deficiency in Vitamin A can cause night blindness and, if untreated, may lead to permanent blindness, especially in children. Insufficient Vitamin A is also linked to diseases like measles and weakened immunity, which makes the body more prone to infections.
10 Foods Rich in Vitamin A
1. Sweet Potatoes. Sweet potatoes are an excellent source of Vitamin A. A 100-gram serving provides up to 19,200 IU of Vitamin A, which significantly exceeds daily requirements.
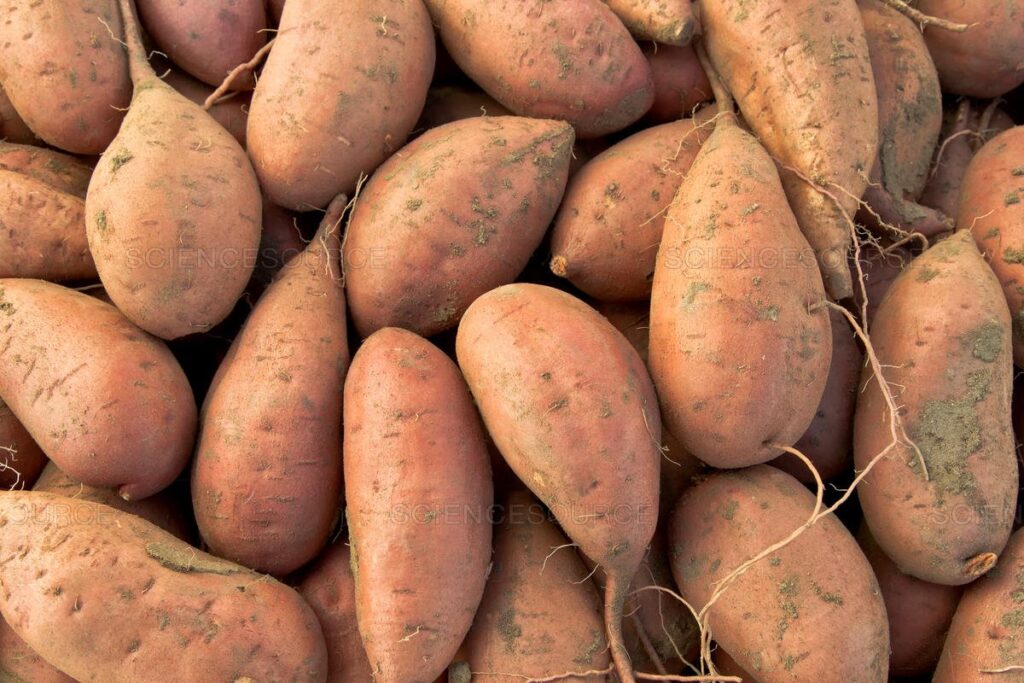
2. Liver. Since Vitamin A is stored in the liver, consuming animal liver provides a rich supply of this nutrient. For instance, 100 grams of beef liver contains approximately 17,000 IU of Vitamin A.

3. Carrots. Carrots are one of the most popular sources of Vitamin A. A 100-gram serving of carrots contains around 17,000 IU of Vitamin A, making it an easy and nutritious snack or side dish.

4. Spinach. Spinach is a leafy green vegetable packed with Vitamin A. A half-cup serving of cooked spinach provides 11,400 IU of Vitamin A.

5. Pumpkin. The bright orange color of pumpkin indicates its rich beta-carotene content, a precursor to Vitamin A. A 100-gram serving provides 11,100 IU of Vitamin A.

6. Cantaloupe Melon. Cantaloupe is a refreshing fruit that also supplies Vitamin A. A half-cup serving contains around 2,700 IU of Vitamin A.

7. Mango. Mangoes, a sweet and abundant fruit in tropical countries like the Philippines, are also rich in Vitamin A. One mango provides approximately 2,500 IU of Vitamin A.

8. Red Bell Pepper. Red bell peppers are not only colorful but also nutritious. A half-cup serving contains around 2,300 IU of Vitamin A.

9. Tomatoes. Medium-sized tomatoes contain about 1,025 IU of Vitamin A. They can be added to salads, soups, or sauces to boost nutrient intake.

10. Lettuce. Lettuce, commonly used in green salads, is another source of Vitamin A. A cup of lettuce provides 361 IU of Vitamin A, contributing to overall daily requirements.

Incorporating Vitamin A-rich foods into your diet is essential for maintaining good vision, boosting immunity, and supporting overall health. By consuming a variety of colorful fruits, vegetables, and animal-based sources like liver and dairy, you can ensure your body receives an adequate amount of Vitamin A. As with any nutrient, moderation is key to avoiding overconsumption while maximizing its health benefits.


