Summary
Bed bug bites are red, itchy welts caused by tiny insects that feed on human and animal blood. These pests, roughly the size of an apple seed or smaller, hide in mattress seams, bed frames, wooden furniture, and crevices, making them hard to detect. They inject a chemical with anesthetic properties when biting, so people often do not feel the bites immediately.
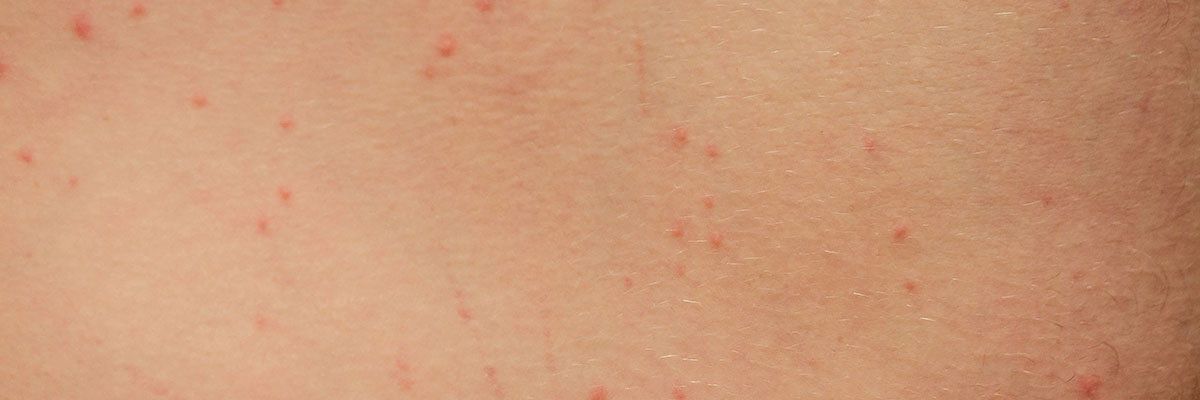
The bites usually appear as clusters or lines of red welts, which can be raised, flat, or fluid-filled. These bites are intensely itchy, and excessive scratching can cause wounds that may lead to skin infections. While most bites heal within one to two weeks with home remedies like antihistamines or topical creams, reactions vary depending on individual sensitivity. Some people may experience severe allergic reactions requiring immediate medical attention.
Although bed bug bites are not typically dangerous and bed bugs do not transmit diseases, they can cause significant discomfort and affect quality of life. Prompt treatment and preventive measures are crucial to managing the symptoms and avoiding further infestations.
Table of Contents
Symptoms of Bed Bug Bites
Studies show that 30% to 60% of people bitten by bed bugs do not experience any symptoms. For those who do, it may take several days after the bite for symptoms to appear. Common symptoms of bed bug bites include:
- Red, swollen welts with a darker center. The bites often appear as small, raised bumps that are redder in the middle and surrounded by inflammation.
- Fluid-filled bumps. In some cases, the welts may contain fluid, resembling small blisters.
- Clustered or linear bite marks. Bed bug bites often appear in lines or clusters, reflecting the insect’s movement while feeding.
- Intense itching. The bites are usually very itchy, which can lead to scratching and potential skin irritation or infection.
- Burning or stinging sensation. Some individuals may experience a burning or painful sensation around the bite area.
Bed bug bites are typically found on exposed areas of the body, such as the face, neck, arms, and hands, as these parts are uncovered while sleeping. However, if bed bugs manage to get inside clothing, they may also bite covered areas, including the chest, back, and legs.
Recognizing these symptoms can help identify bed bug bites and differentiate them from other insect bites or skin conditions. Prompt treatment can alleviate discomfort and reduce the risk of secondary infections caused by scratching.
Diagnostic Procedures for Bed Bug Bites
Diagnosing bed bug bites involves identifying the characteristic signs of bites, evaluating the affected environment for evidence of infestation, and ruling out other potential causes of the symptoms. Below are the primary diagnostic procedures for bed bug bites:
- Physical examination of the bites. A healthcare professional will examine the bite marks, which often appear as red, itchy welts in clusters or straight lines. The distribution of bites on exposed skin, such as the face, neck, arms, and hands, can help differentiate them from other insect bites.
- Assessment of symptoms. Symptoms such as itching, swelling, or irritation, along with a history of exposure to environments where bed bugs may be present, are considered during the diagnosis. Allergic reactions or secondary infections from excessive scratching may also be evaluated.
- Inspection of the sleeping area. To confirm bed bug bites, it’s essential to check the sleeping environment for signs of infestation. This includes looking for live bed bugs, reddish-brown stains on bedding (from crushed bugs or blood), shed skins, or eggs in mattress seams, bed frames, and furniture cracks.
- Ruling out other causes. Conditions such as mosquito bites, flea bites, scabies, or allergic reactions can mimic bed bug bites. A thorough evaluation helps rule out these alternatives and confirm that the bites are from bed bugs.
- Use of monitoring tools. In cases where bed bugs are suspected but not immediately visible, traps or monitors may be used to capture evidence of their presence. These tools can confirm an infestation and identify its severity.
While there is no specific medical test to diagnose bed bug bites, the combination of clinical evaluation, environmental inspection, and exclusion of other causes provides a reliable diagnosis. Early identification and addressing the source of the infestation are critical to preventing further bites and managing symptoms effectively.
Complications of Untreated Bed Bug Bites
While bed bug bites are not typically life-threatening, leaving them untreated or ignoring the underlying infestation can lead to several complications, both physical and psychological. Below are the potential issues that can arise from untreated bed bug bites:
- Secondary skin infections. Excessive scratching of itchy bites can break the skin, leading to bacterial infections such as impetigo or cellulitis. Infections can cause redness, swelling, pain, and pus formation, requiring medical treatment.
- Allergic reactions. Some individuals may develop severe allergic reactions to bed bug bites, including hives, intense swelling, or, in rare cases, anaphylaxis. These reactions can become dangerous without prompt medical intervention.
- Sleep disturbances. The discomfort and anxiety caused by bed bug bites can lead to insomnia, poor sleep quality, or chronic fatigue, affecting overall health and well-being.
- Psychological stress and anxiety. Bed bug infestations and recurring bites can cause significant emotional distress, anxiety, or even paranoia. Persistent infestations may lead to conditions like post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in severe cases.
- Scarring and skin discoloration. In some cases, especially if bites are scratched excessively or become infected, the skin may develop scars or hyperpigmentation that can be permanent.
- Worsening of pre-existing conditions. People with chronic skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis, may experience flare-ups or worsened symptoms due to the irritation and scratching caused by bed bug bites.
- Spread of the infestation. Ignoring the bites without addressing the source can allow bed bugs to multiply and spread, making eradication more challenging and increasing the risk of further complications.
Though bed bug bites are generally not dangerous, untreated bites and infestations can lead to significant discomfort and other health concerns. Proper treatment of bites and prompt action to eliminate infestations are essential to minimize these risks.
Causes of Bed Bug Bites

Bed bugs are often introduced to a place when they hitch a ride on clothing, shoes, or luggage. They can also be brought into homes through secondhand items, such as infested mattresses, pillows, bedding, furniture, and other household items. This makes it easy for bed bugs to spread, even in clean environments.
Contrary to the misconception that bed bugs only infest unclean spaces, these pests can thrive anywhere once introduced. They are adept at hiding in small crevices, cracks, and seams, making them difficult to detect. A single female bed bug can lay 200 to 500 eggs in her lifetime, leading to rapid population growth if not addressed.
Bed bugs are also highly resilient. They can survive for over a year without feeding, waiting patiently for a new host to provide the blood meal they require. This makes it essential to thoroughly inspect and treat areas where bed bugs might be present, especially when acquiring used items or traveling. Proactive measures and vigilance are key to preventing infestations.
Prevention of Bed Bug Bites

To avoid bed bug bites, it’s essential to maintain a clean and organized home, particularly in bedrooms and areas where mattresses are used. Implement the following strategies to prevent and control bed bugs:
- Regularly change and inspect beddings. Frequently replace and examine bedsheets, pillowcases, and blankets for any signs of bed bugs or their eggs.
- Wash beddings in hot water. Use hot water to launder beddings and other fabrics that may harbor bed bugs. High temperatures effectively kill bed bugs and their eggs.
- Vacuum mattresses and furniture thoroughly. Clean mattresses, bed frames, and upholstered furniture with a vacuum cleaner. Pay special attention to cracks, seams, and crevices where bed bugs commonly hide.
- Avoid storing items under the bed. Keep the area beneath your bed clutter-free, as stored items can provide hiding spots for bed bugs.
- Inspect and clean travel items after trips. When returning from vacations or trips, wash worn clothes and clean luggage and shoes thoroughly. Bed bugs can latch onto these items and hitch a ride back to your home.
Regular inspections and proper hygiene practices are key to keeping bed bugs at bay. By taking these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of an infestation and the discomfort caused by bed bug bites.
Risk Factors for Bed Bug Bites

The likelihood of being bitten by bed bugs increases in crowded or high-traffic areas where people frequently come and go. These environments provide opportunities for bed bugs to spread and thrive. Common places where bed bugs are more likely to be found include:
- Rental properties. Shared living spaces, such as apartments and boarding houses, are prone to infestations due to high tenant turnover and shared furniture.
- Hotels. Bed bugs are often introduced by travelers, making even the cleanest hotels susceptible to infestations. They can hide in mattresses, bed frames, and luggage.
- Ships. Cruise ships and other passenger vessels, where people share cabins and common spaces, can harbor bed bugs brought on board by passengers or crew.
- Trains and buses. Public transportation systems with upholstered seats and high passenger turnover provide hiding spots for bed bugs, which can transfer between commuters.
- Evacuation centers. Overcrowded emergency shelters with shared sleeping arrangements and bedding can facilitate the spread of bed bugs.
- Hospitals. Despite their cleanliness standards, hospitals can host bed bugs brought in by patients, visitors, or staff.
- Movie theaters. Bed bugs can hide in the fabric of theater seats, where they latch onto clothing and bags.
Even in well-maintained spaces, the presence of bed bugs cannot be entirely ruled out, as they can hitch a ride on travelers or their belongings. Vigilance and regular inspections are essential, particularly in public and shared environments, to minimize the risk of exposure to bed bugs.
Bed Bug Bites FAQs
Bed bug bites can be a source of discomfort and confusion for those affected. Understanding how these pests behave, their bites, and how to deal with them is essential for effective management. Here are some frequently asked questions about bed bug bites, along with clear and helpful answers.
- What do bed bug bites look like?Bed bug bites typically appear as small, red, itchy welts. They are often found in clusters or straight lines and may be raised, flat, or filled with fluid.
- Where on the body do bed bug bites occur?Bites usually occur on exposed skin areas such as the face, neck, arms, hands, and feet. However, bed bugs can also bite covered areas if they crawl under clothing.
- Do bed bug bites hurt?Most people do not feel the bites initially because bed bugs inject an anesthetic when feeding. The bites may become itchy or sore a few hours to days later.
- Are bed bug bites dangerous?While bed bug bites are not typically harmful, they can cause intense itching, which may lead to secondary infections if scratched excessively. Some individuals may also experience allergic reactions that require medical attention.
- How long do bed bug bites take to heal?Bed bug bites usually heal within one to two weeks. Applying antihistamines or hydrocortisone cream can help alleviate itching and discomfort.
- Do bed bugs spread diseases?Unlike mosquitoes or ticks, bed bugs are not known to transmit diseases. However, their bites can cause psychological stress and physical irritation.
- How can I tell if bed bugs are present in my home?Look for signs such as small reddish-brown stains on bedding, shed skins, or the bugs themselves in mattress seams, furniture cracks, or other hidden areas.
- How can I prevent bed bug bites while sleeping?Encase your mattress and pillows in bed bug-proof covers, wash and heat-dry bedding regularly, and inspect your sleeping area for signs of infestation.
- What should I do if I suspect bed bugs in my home?Contact a pest control professional to inspect and treat your home. Avoid moving items that may spread the infestation to other areas.
- Can bed bugs survive in clean homes?Yes, bed bugs can thrive in any environment where they have access to hosts for feeding. Cleanliness does not prevent an infestation but can make detection easier.