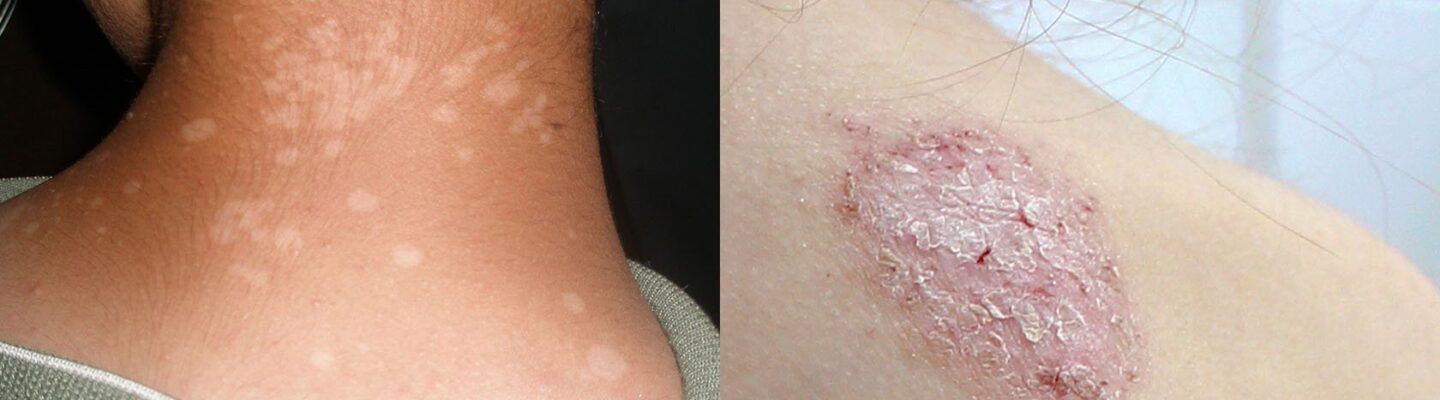
Skin infections like buni (ringworm) and an-an (tinea versicolor) are common fungal conditions that can cause confusion due to their overlapping symptoms. While both are caused by fungi and respond to similar treatments, they have distinct characteristics that set them apart.
Can An-an Appear on the Elbow?
Yes, an-an, also known as tinea versicolor or “white spots,” can occur on various parts of the body, including the elbows. It most commonly appears on the back, chest, arms, and thighs, but it can spread to less typical areas under certain conditions. An-an manifests as small, white, or discolored patches on the skin, often with mild scaling but without itching or irritation.
What is Buni?
On the other hand, buni or ringworm appears as circular, red, scaly patches that may itch. Unlike an-an, buni often has a distinct raised border, and the center of the patch may appear clearer than the edges, giving it a “ring-like” appearance.
Key Differences Between Buni and An-an
- Appearance.
- Buni: Circular, red, and scaly patches, often itchy.
- An-an: Flat, discolored patches (usually white, but may also be brown or pink), not itchy.
- Affected Areas.
- Buni: Can occur anywhere on the body, including the scalp, groin, and feet.
- An-an: Commonly found on the upper body, arms, and thighs but can also spread to other areas.
- Cause.
- Both conditions are fungal in nature but caused by different species of fungi.
Treatment for Buni and An-an
Despite their differences, both buni and an-an are treated with similar antifungal medications. Over-the-counter antifungal creams or ointments are often effective in resolving the infection.
Examples of antifungal treatments include:
- Ketoconazole. An antifungal cream that helps eliminate the fungus causing the infection.
- Clotrimazole. Effective in treating a variety of fungal infections, including buni and an-an.
- Terbinafine. A potent antifungal agent that works well for stubborn cases.
Apply the cream to the affected area twice daily for 1 to 2 weeks or as directed by a healthcare provider. While most cases can be treated at home, seeking guidance from a dermatologist is recommended for proper diagnosis and treatment, especially if the infection is widespread or recurrent.
Understanding whether you have buni or an-an is crucial for effective treatment, but it’s reassuring to know that both conditions are manageable with similar antifungal medications. If symptoms persist or worsen despite treatment, consult a dermatologist to rule out other skin conditions and receive tailored medical advice. Early treatment ensures faster recovery and prevents the infection from spreading to other parts of the body or other people.