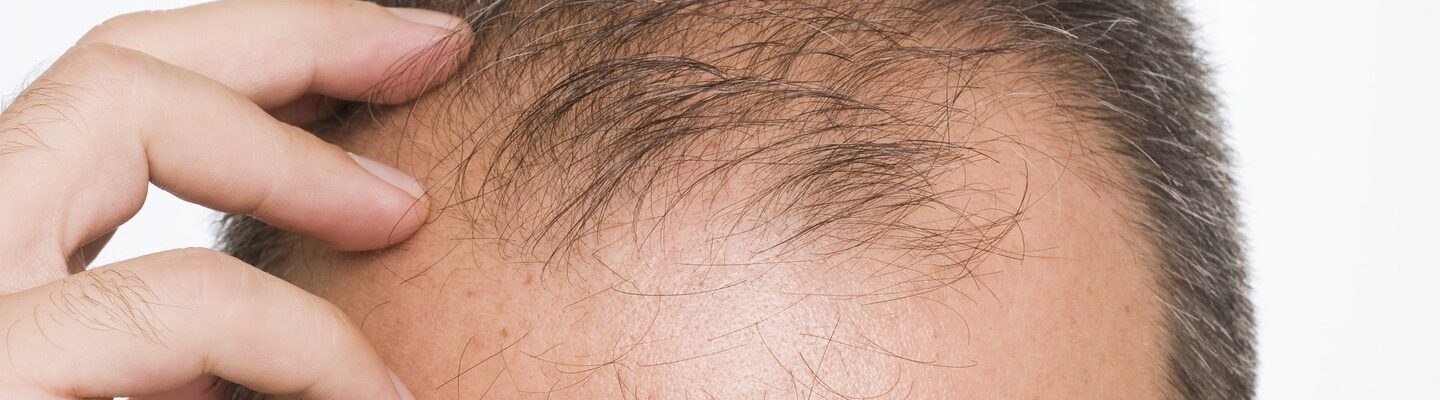
Baldness, particularly among men, is a common occurrence and primarily hereditary. Known as male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia), it is caused by genetics, hormone levels, and aging. Here are the main factors influencing hair loss:
- Genetics and Family History. Your chances of balding depend on your family background. If your father, grandfather, or other male relatives experienced baldness, you’re likely to follow a similar pattern. Knowing when they began to lose hair can give you an idea of when it might start for you.
- Ethnicity and Genetics. Different ethnic groups have varying tendencies for baldness. For instance, Caucasian and Filipino men may experience earlier or more severe hair loss compared to others.
- Stress and Lifestyle Factors. While genetics play a dominant role, stress, anxiety, and overworking yourself can exacerbate hair loss. Excessive mental and emotional strain may accelerate thinning hair, though it is not the primary cause.
- Medical Conditions and Treatments. Hair loss due to illness, such as thyroid disorders, infections, or cancer treatments like chemotherapy, differs from natural baldness.
Patterns of Male Baldness
Male pattern baldness follows a predictable progression. It usually begins in one of two areas:
- Receding Hairline. Balding starts at the temples, gradually moving backward and creating an “M” shape.
- Crown Baldness. Hair loss begins at the center of the scalp, often forming a circular bald spot.
Over time, these two areas can meet, leaving a rim of hair on the sides and back of the head or leading to complete baldness.
Debunking Myths About Baldness
Several misconceptions surround male baldness. Let’s clarify the truth:
- Baldness is not caused by sexual activity or masturbation. Hair loss has no connection to sexual frequency, libido, or physical activity.
- Tight hats do not cause baldness. Wearing hats or helmets does not “suffocate” the scalp or lead to permanent hair loss.
- Bald men are not “better” or “worse” in bed. This is a stereotype with no scientific basis.
How to Prevent or Manage Baldness
While genetic hair loss cannot be fully avoided, there are ways to slow its progression and manage its impact:
- Use Medications.
- Minoxidil. This topical solution is applied daily to the scalp to stimulate hair growth and slow hair loss. It is available over-the-counter.
- Finasteride. An oral medication that blocks DHT (a hormone linked to hair loss), Finasteride helps maintain existing hair and, in some cases, regrow lost hair.
- Style to Hide Baldness.
- Some individuals comb remaining hair strategically to cover thinning areas.
- Wearing wigs or hairpieces is another effective way to maintain a full-hair appearance.
- Shave and Embrace It.
- Many men choose to fully shave their heads when baldness becomes noticeable. Embracing baldness can boost confidence and even create a more youthful, clean look.
- Address Stress and Health.
- Managing stress, maintaining a healthy diet, and exercising regularly can support overall hair and scalp health.
While hair loss can feel concerning, it is a natural part of aging and male development. For many, baldness becomes a symbol of confidence and maturity. Teenagers today often choose to shave their heads by choice—proving that a clean, bald look can be stylish and empowering.
If baldness is affecting your confidence, you can choose to treat it, hide it, or embrace it. Whatever your decision, remember that baldness is common, natural, and does not define your worth or appearance. Who knows? Going bald might even give you a fresher, younger look.